HerbMedX


Eczema is the most common chronic inflammatory skin disease. The most important symptoms of this disease include inflammation, dryness, severe itching and increased skin sensitivity. In some cases, atopic dermatitis causes frequent rashes, persistent scratching, erythematous plaques, and small blister that may be accompanied by extracellular fluid leakage
ECZEMA
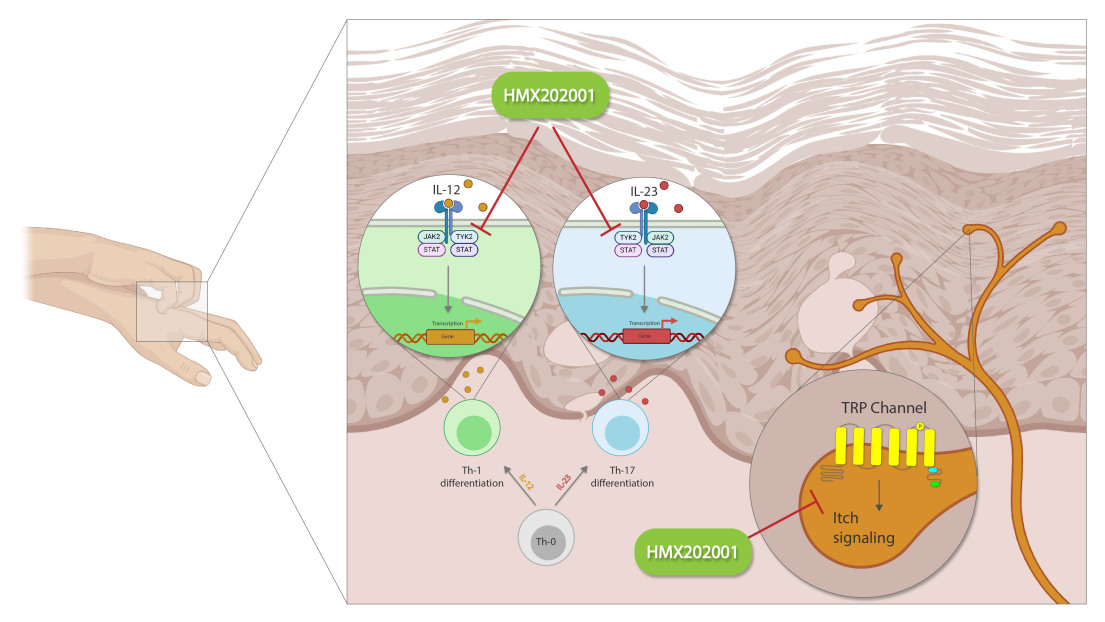
HMX202001 is a novel TYK2 & TRP channels inhibitor for Eczema
The etiology of this disease has not yet been fully determined; But it is probably a set of factors such as genetic factors, disturbance in the physical barrier of the skin and especially disturbance in the balance of inflammatory responses and response to allergens. Local anti-inflammatory drugs such as corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and systemic antihistamines are commonly used in the treatment of eczema. But the long-term use of these drugs may cause several side effects such as skin atrophy, severe itching, burning sensation, thinning of the skin, bleeding and resistance to the drug
Several inflammatory cytokines play a role in the pathogenesis of eczema, and many of these cytokines require the activation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway to play their parts. TYK2 is a member of the JAK kinase family, which plays a role in the signaling pathway of IL-12, IL-23, and type I IFNs. In the beginning and acute phase of the disease, IL-4 and IL-13 cytokines can activate B cells and cause antibody class switching for IgE. IgE secreted from plasma cells by binding to FcεRI on the surface of mast cells and basophils leads to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines from these cells. IL-23 affects the differentiation and survival of Th17, which plays a vital role in inflammatory diseases because of the secretion of IL-17, IL-1, and TGFB cytokines. Due to the importance of TYK2 in inflammatory cytokines signaling, TYK2 inhibitors have been used in several inflammatory diseases such as Psoriasis, Lupus, Crohn's, Psoriatic arthritis, and Ulcerative colitis
HMX202001 Target


HMX202001 consists of Pistacia atlantica polyflavonoid plant extract, which is widely used in the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Pistacia atlantica plant is found in the Zagros mountains of Iran (west and north-west of Iran with moderate climate). So far, several studies have reported its high flavonoid content and chromatographic studies have isolated several flavonoids such as Quercetin, Rutin, Kaempferol, Apigenin, and Luteolin. Due to the high phenolic content of the tuber plant, it is among the first 50 food products with antioxidant potential.
HMX202001 content